What is radio tomographic imaging?
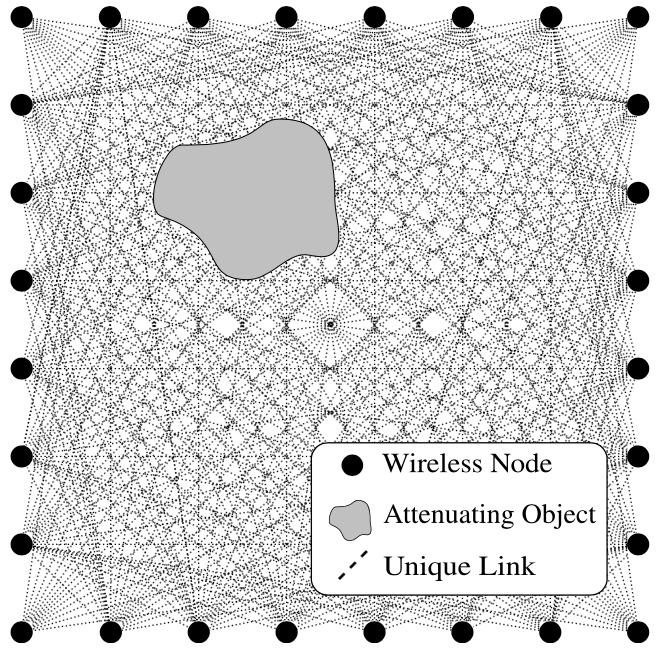
Radio Tomographic Imaging (RTI) is an emerging technology for imaging passive objects (objects that do not carry a transmitting device) with wireless networks [1]. The key source of image is Received Signal Strength Index(RRSI) which has a nature that it decreases(usually) when objects disturb the going ahead radio signal.
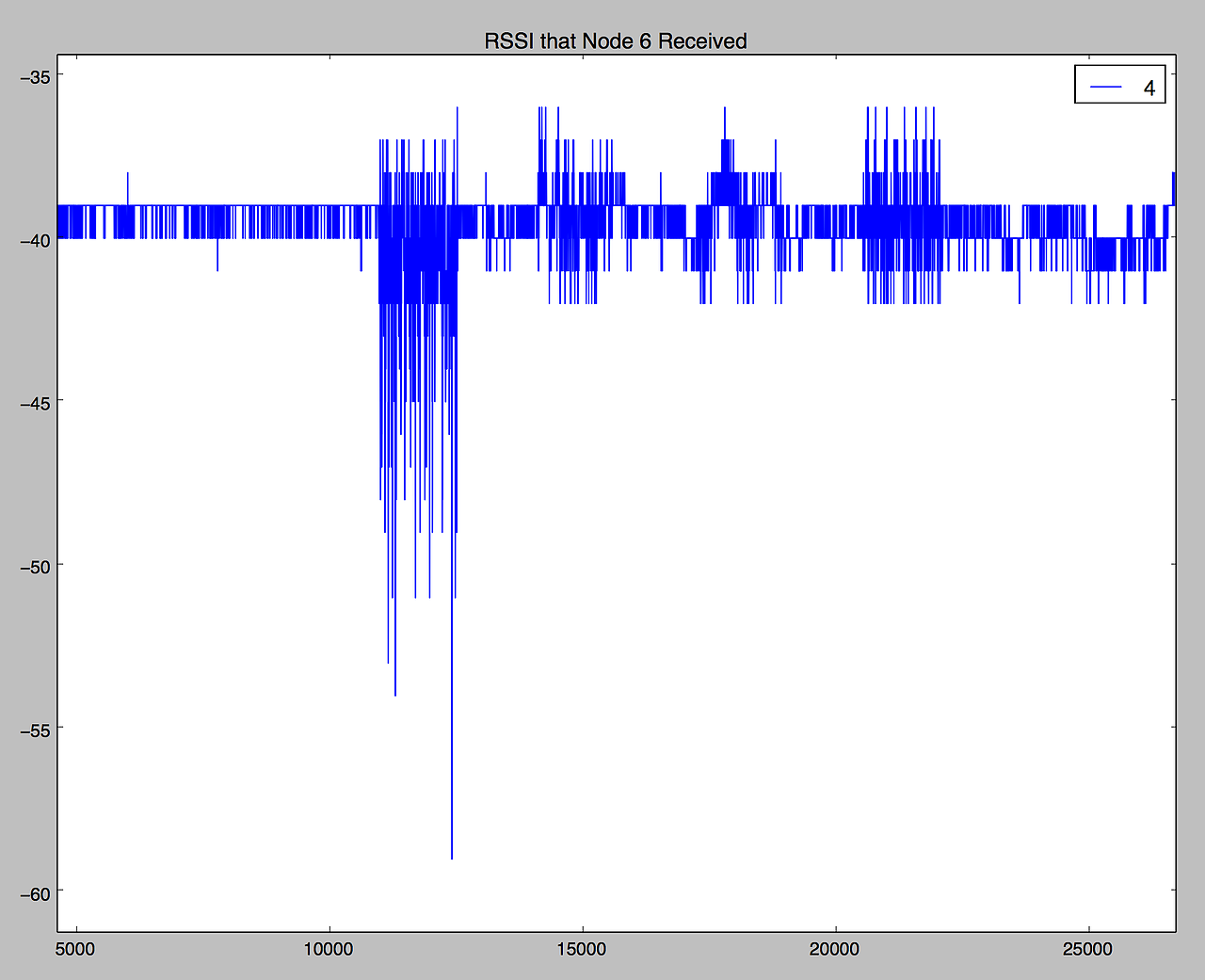
The picture above shows the RRSI values as time goes by, and there are some changes up and down at certain times because of a moving object. In fact, the graph was obtained from short experiments when the experimenter move around the nodes. In the radio tomography network, all of the nodes makes a lots of RSSI data extremely fast and by using the data, images are created.
Working as a intern in CSIRO, I was on project regarding radio tomography. The purpose of this project is developing radio tomography system by using low power sensor network device. For this, I used TI Sensortasg cc2650 as a low power device. and I used Contiki-OS for device application OS for radio tomography system.
There are two major steps for Developing Radio Tomography using low power network device. First one is to develop the device application that I use, TI Sensortag. Next one is to reconstruct image form data that collected by using network devices.
I implemented Contiki device application for nodes that consist the Radio Tomography Network. I also implemented Contiki device application of master node that schedules the other nodes and collects data from the network. Next, I deployed the nodes around target area so the radio signal can pass through the area. I collected raw data of RSSI of each node in the radio tomography network and reconstructed image of the area.
Node scheduling concepts of the device application and reconstruction algorithm will be covered in the next chapters.
_____________
[1] Wilson, Joey, and Neal Patwari. “Radio tomographic imaging with wireless networks.” IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 9.5 (2010): 621-632.